Describe the Large Scale Structure of the Universe
But these researchers were. Large-scale structure of the cosmos.

Structure Of The Universe Universe Today
Zeldovich tronomers have long recognized.

. The cone on the left shows one-half of the 2dFGRS which determined distances to more than 220000 galaxies in the southern sky out to a depth of 2 billion light years. For example galaxies behind a galaxy cluster are attracted to it and so fall towards it and so are slightly blueshifted compared to how they would be if there were no cluster On the near side things are slightly. Other researchers have considered the use of galaxy clusters to probe large scale structure in the universe as well.
Each of the 9325 points represents a galaxy. Baryonic matter in the universe comprised of about 75 Hydrogen and 25 Helium by mass. This observation implies that galaxies are clustered on at least 15h1 Mpc scale with a correlation scale of ro gg 5h1 Mpc where ξ r rro 18 Ar 18.
The Large Scale Structure LSS of the universe refers to the patterns of galaxies and matter on scales much larger than individual galaxies or groupings of galaxies. We review the formalism and applications of non-linear perturbation theory PT to understanding the large-scale structure of the Universe. Galaxy cluster are distributed evenly throughout space with no large gaps There are many more galaxies and clusters in some directions up and down the milky ways disk and very few galaxies in.
A fundamental principle of cosmology the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe is that on large enough scales the Universe is homogeneous looks the same wherever you are and isotropic looks the same in whatever direction you look. We first discuss the dynamics of gravitational instability from the linear to the non-linear regime. The Large-Scale Structure of the Universe Across blllions of light-years space is a honeycomb of galactic superclusters and huge voids.
The idea of whether galaxies are distributed uniformly in space can be traced to Edwin Hubble who used his catalog of 400 extragalactic nebulae to test the homogeneity of the Universe Hubble 1926 finding it to be generally uniform on large scales. The evolution of density inhomogeneities and the velocity field in an expanding continuous medium is studied. Large scale structure is defined as the structure or inhomogeneity of the Universe on scales larger than that of a galaxy.
The consideration is based on the model equation of non-linear diffusion Burgers equation that together with the equation of continuity incorporating mass density gives an approximate description of density inhomogeneity growth at the advanced non-linear. Describe the large-scale structure of the universe as revealed by redshift surveys of galaxies. This is one of the largest observed structures in the Universe containing over 10000 galaxies and stretching over more than 137 billion light years.
This is one of the largest observed structures in. Szalay and Yakov B. They find 15h1 Mpc with correlations that drop to the level of the noise for ξgg r 20r 18 for r larger scales.
The field of large-scale structure is still growing rapidly fromthe infusion of new data and even more ambitious surveys are nowin the planning stages. The structure may result from perturbations in the density of matter early in the big bang by Joseph Silk Alexander S. After the arrangement of protons neutrons and electrons the universe extended and cooled enough that no more molecule development happened anyway with temperatures still exceptionally high this recombination period is the thing that happened and brought about an atomic response.
At this scale there is also a distinct pattern of motion. In physical cosmology the term large-scale structure refers to the characterization of observable distributions of matter and light on the largest scales. This includes Eulerian and Lagrangian PT non-linear approximations and a brief description of.
Office DEPOT estions Chapter 16 - Set 2 1. The Universe exhibits structure over a wide range of physical scales from satellites in orbit around a planet through to the galaxy superclusters galactic sheets filaments and voids that span significant fractions of the. List the observational pieces of evidence that might be found to distinguish an active galaxy from a normal galaxy.
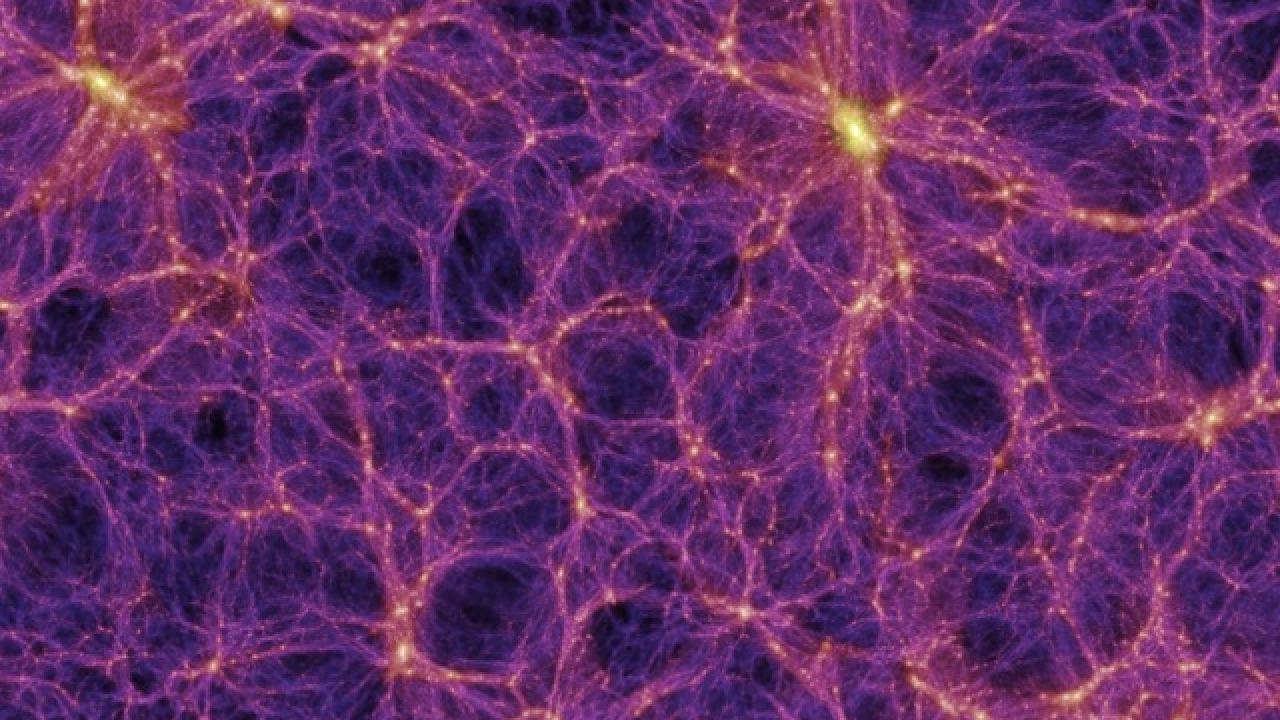
Describe what voids are and what they tell us about the large-scale structure of the universe. Prospects also exist for improvement in theaccuracy of the distance indicators for galaxies. The large-scale structures of sheets filaments voids and galaxy superclusters are clearly visible and give this region of space a honeycomb appearance.
The large scale structure of the Universe. The areas devoid of galaxies range from 100 to 400 million light years across. What is the Large Scale Structure of the Universe.
Note the wall and bubble like distributions of galaxies. CaptionThe large-scale structure of the Universe is made up of voids and filaments that can be broken down into superclusters clusters galaxy groups and. At this point you start seeing the large-scale structure of the Universe in which clusters and super-clusters of galaxies are arranged in a pattern of filament structures.
Describe what voids are and what they tell us about the large-scale structure of the universe. Slices of the northern and southern galactic hemispheres. This is pretty much how the Universe looks as far into the distance as we can see.
Download PDF Abstract. Linear or wall like distributions of galaxies. These correlated structures can be seen up to billions of light years in length and are created and shaped by gravity.
The large-scale structure of the universe also looks different if one only uses redshift to measure distances to galaxies. We are situated at the centre of the figure. Drawn to the same scale is a small section of the SDSS in which an even larger Sloan Great Wall has been identified 100.
At The Largest Scales Our Milky Way Galaxy Is In The Middle Of Nowhere Universe Today
No comments for "Describe the Large Scale Structure of the Universe"
Post a Comment